
The strength of the New Zealand Dollar (NZD) has been badly affected recently. NZD performance vs USD, CAD, and CHF, has been impacted by a combination of domestic and international factors. This trend was seen throughout 2023 and this has broadly continued to be the case in early 2024. January has seen a drop in the strength in NZD against a basket of currencies. These include NZD to USD (NZD is down 4.2% against USD), and CAD to NZD (NZD is down 2.1% against CAD).
Lets explore some of the fundamental factors at play.
Economic Conditions Affecting NZD
High inflation rates within New Zealand have been a significant factor. Food product inflation has exceeded 12% and other categories like fruits, vegetables, meat, poultry, and fish have also seen substantial price increases. This inflationary pressure has contributed to reduced consumer spending and a weakening real estate market.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand‘s monetary policy, particularly the aggressive tightening and raising of the official cash rate to 5.5% to combat inflation, has had a notable impact. This action aimed to reduce inflation from a 30-year high. However the decision to halt rate hikes amid continuous increases by other central banks has not favored the NZD.
Commodity Prices and Global Demand
The prices and demand for New Zealand’s largest exports to China have also affected the NZD’s strength. Decreases in dairy prices, by 3.1% in July and 20% year-over-year, alongside reduced demand from China due to its economic downturn, have negatively impacted the NZD.
NZD Technical Analysis
From a technical standpoint, the NZD/USD has been following a strong downtrend. Indicators like exponential moving averages (EMA) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) supporting a bearish outlook. Further declines based on technical patterns and market sentiment analysis have been predicted.
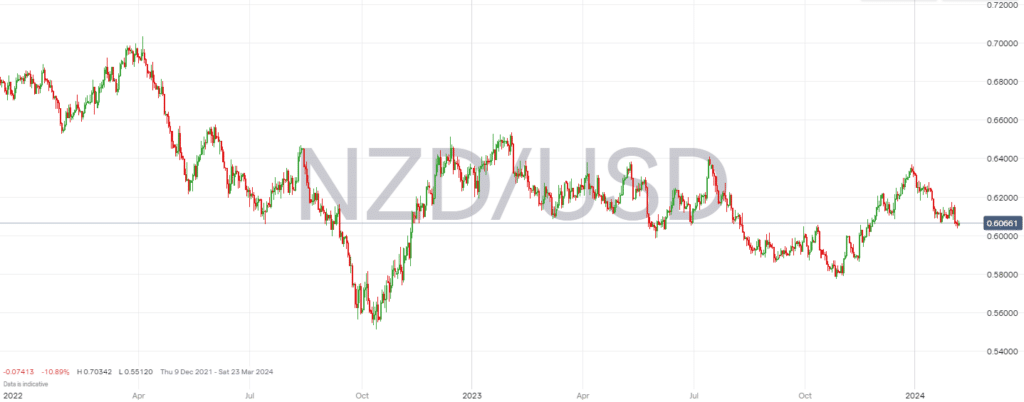
Global Economic Outlook
Internationally, the continued strength of the US Dollar, weakening global growth, and the impact of global economic conditions, including the outcomes of the International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) forecasts for slower global growth, have influenced the NZD. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand’s (RBNZ) response to these conditions, including keeping interest rates steady at high levels to fight inflation, also plays a critical role.
Interest Rate Differentials
The difference in interest rate paths between New Zealand and its trading partners, particularly the US, has applied downward pressure on the NZD. The higher interest rates in the US, alongside lower commodity prices for New Zealand exports, have reduced demand for the NZD.
Overall, domestic economic challenges, such as high inflation and the RBNZ’s monetary policy stance, have had an impact on NZD. Added to this you have international factors like global economic slowdown and commodity price shifts. You can clearly see the impact on NZD’s performance against currencies like the USD, CAD, and CHF.
Related Articles
 Between 74-89% of CFD traders lose
Between 74-89% of CFD traders lose  Your capital is at risk
Your capital is at risk  Your capital is at risk
Your capital is at risk  Your capital is at risk
Your capital is at risk