

For the past two decades, foreign exchange or forex trading has increased dramatically in popularity across the globe. However, the current system of floating currency pairs recently celebrated its 50th anniversary without much fanfare. How many forex traders today know that freely floating currencies only came into being in March 1973?
This financial transition did not happen overnight. Traders today may enjoy the stability that currency markets offer, but without a strong US Dollar, a dynamic economy to back it up, and concurrence by the international community, the currency market that we know and enjoy may not have evolved to its present state today.
The Strategic Importance of the US Dollar
Undoubtedly, the US Dollar is the most important and strategic currency traded in the forex market. The US Dollar is a part of forex currency pairs that account for over 88% of trading volume in the market. Based on the most recent triennial survey published last year by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), the global forex market has an average daily turnover of $7.5tn, the largest capital market in the world.
This daily volume figure dwarfs figures for international trade, which requires a stable currency market to transact business. Treasury managers across the globe hedge risk exposures related to cross-border contracts to drive a small portion of the transaction turnover, but the balance relates purely to speculation. Speculators drive the inefficiencies out of exchange rate valuations, allowing for tight ranges and a stable trading market.
Understanding how the US Dollar became strategically important requires a brief history lesson. The United States was the only nation that fought in World War II that did not suffer decisive physical damage to its mainland infrastructure. All the other countries involved were forced to rebuild, which left their economies in disarray. Some nations became indebted to the United States for their assistance.
Related Articles
Shortly before the end of the war in 1944, the US Dollar became the currency selected at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, for which gold was convertible for free at $35 per ounce. All other leading currencies were then rooted to the dollar with fixed ranges of fluctuation. After Bretton Woods, the US Dollar was the most stable and trustworthy currency for many years until all currencies were allowed to float freely against each other. This transition occurred in the early 1970s after the United States unilaterally ended the convertibility of its currency into gold.
Subsequently, trade agreements and associated debt instruments were predominantly denominated in US Dollars. A country’s ability to trade in international markets and obtain credit was then dependent upon the amount of currency reserves held in its central bank. As you might expect, the US Dollar became by far the top reserve currency in the world in terms of the percentage of global currency reserves. The Dollar accounts today for an estimated share of 60% of the total global currency reserves held in central banks, as per the chart presented below:
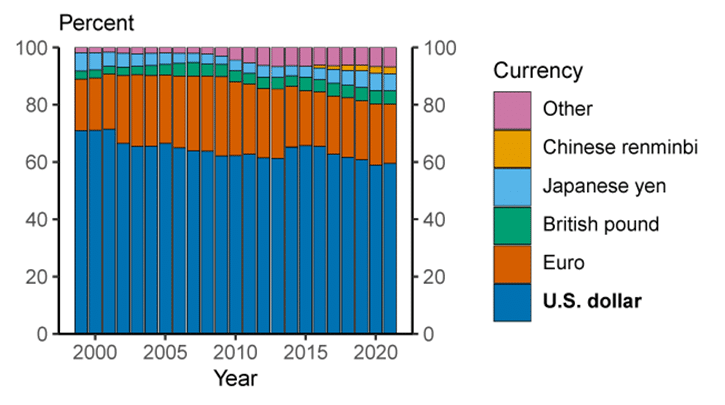
Chart courtesy of www.FederalReserve.gov
International debt instruments of many countries that are actively trading in the global market are now, in large part, denominated in US Dollars. That is primarily due to the establishment of institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank that also arose out of the Bretton Woods conference. Consequently, any repayment of a USD-denominated loan or attempt to stabilise the national currency would tend to necessitate trading US Dollars on the open market.
From the Gold Standard to Floating Exchange Rates
The currency or foreign exchange market has evolved slowly to become the largest capital market in the world, where all major currencies are actively traded in a system of floating exchange rates. The following paragraphs cover a brief history of the currency market. Included is the evolution from commercial transactions involving currency of intrinsic value like gold – the gold standard – to the more modern usage of paper fiat currency that is backed, simply, by the credit of the country printing it.
As commercial interactions between different countries increased in early human civilized history, a globally standardized medium of exchange was required to facilitate commercial transactions. The first accepted medium of exchange consisted of precious metals, gold and silver. This primitive currency gave rise to the minting of coins during the Roman era, which matured into issuing paper currency in the Middle Ages.
Paper money was initially introduced to represent the value of gold for security purposes. Gold would first be deposited into a trusted bank, and a receipt would then be issued for the amount of gold on deposit that could be used as a medium of exchange in place of the precious metal.
These receipts eventually became the principal exchange instruments, so governments began to issue currency backed by the country’s gold reserves. This later became the first international monetary standard, the Gold Standard.
The origins of the Gold Standard in international commerce began in 19th century Britain after the English Monarchy adopted the Gold Standard in 1816. Silver was also used as a standard means of exchange. Nevertheless, the price of silver was pegged in relation to gold. By the beginning of the 20th century, all major industrial powers had converted to the gold standard with a set amount of gold backing a specified amount of currency.
The start of the First World War brought an end, at least temporarily, to the gold standard. The enormous amount of capital needed to fund military defence projects against the German aggressors was far beyond the amount of gold available to back all of the currency. As nations began ignoring the gold standard and no longer defined the values of their currencies in terms of gold, mass speculation in the currency markets soon followed.
People Also Read
- Investing Through a Constitutional Crisis
- How to Use Consumer Confidence Reports in Forex Trading
- What are the Most Volatile Forex Pairs?
Bretton Woods Conference Convenes to Find Alternative to the Gold Standard
World War II exacerbated the existing problems with the Gold Standard and led to a global conference to determine a suitable path going forward. Before the end of World War II, the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference was held in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, in 1944. The meeting brought together delegates from all Allied nations, who then worked out and signed the Bretton Woods Accord. The Accord effectively pegged the price of gold to $35 US Dollars per ounce and all other currencies to the US Dollar with a maximum deviation of 1%.
As the United States accumulated massive budget and trade deficits during the 1950s and 1960s, the US Dollar began losing its status as the world’s only reserve currency. Also, Richard Nixon, then the US President, decided to end the Dollar’s convertibility into gold in August of 1971, essentially taking the US Dollar off the Gold Standard. The need for stable exchange rates persisted, and several mathematical methods were developed to minimise exchange rate movements. None of these methods proved suitable for the task at hand.
As currency pressures came to a head, most major nations decided to allow their currencies to float freely by March 1973. This was the beginning of the modern-day fluctuating exchange rate system, but countries continued experimenting with controlled exchange-rate systems after 1973. One attempt that has worked is the Euro, where twelve European nations decided to replace their national currencies with the Euro in 2002. Forex traders can access this global Interbank market of floating currency pairs via a multitude of online forex market makers.
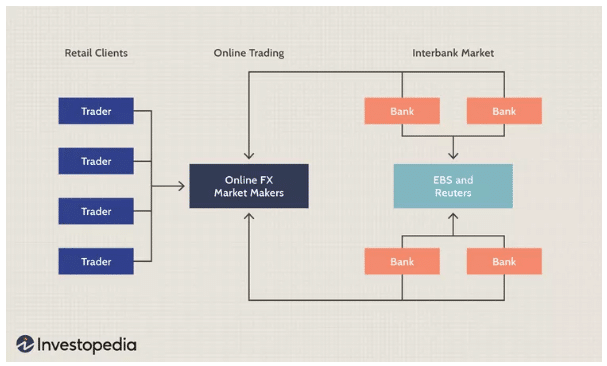
Diagram courtesy of www.investopedia.com
Today exchange rates float freely for most major currencies depending on supply and demand pressures, and no major paper currencies have their values fixed to the price of gold or other hard assets. In the process, the shift to floating exchange rates spawned today’s massive foreign exchange market, providing ample trading opportunities for forex speculators with its active exchange rate fluctuations and notable trends in many currency pairs.
Reserve Currencies – Definition and Trends
A reserve currency is held by central banks to pay their international debts or to use to influence the exchange rate of their country’s currency. Reserve currencies can also be used to pay for vital international trade commodities like gold and oil. The IMF has established reserve management policy standards to ensure that countries can meet their external trade obligations and to maintain confidence in global forex markets.
The global reserve currency since the early part of the last century has been the US Dollar, which was pegged to the value of gold for much of that time as it adhered to the so-called Gold Standard. This key role for the Dollar was further supported during the Bretton Woods period of pegged exchange rates that extended from after the end of World War II to the early 1970s when President Richard Nixon unilaterally took the US Dollar off the gold standard.
Central banks have shifted their allegiances to various currencies in their respective reserve portfolios from time to time, but these reallocations have never been material in nature. The USD still reigns supreme, and the United States benefits from this global support, which helps to keep the US Dollar strong over time and gives the US what appears to be unlimited borrowing power. Its debt instruments are held by a host of central banks at below-market interest rate levels.
Why is the US Dollar the Reserve Currency of the World?
The US Dollar (USD) is the world’s reserve currency. Despite its tumultuous recessions, stagflations, bull and bear markets, and wars, the US Dollar has shown remarkable resilience as the world’s measure of value. What is behind the tremendous staying power of the currency? What makes a currency a global definition of value?
The leading cause of the dominance of a nation’s currency is, of course, its economic power. The greater a country’s Gross Domestic Product and trade volume, the greater the demand for its currency. But beyond the economy’s health, the nation must be a centre of demand so that its currency will be readily available, supported by strong consumerism, and not dampened by government intervention. Such has been the case with both the British Pound and the US Dollar in this and the last century. In the past, gold production or its accumulation was also an essential factor.
Nations tend to trade with others with which they have overall good relations. The power behind a dominant currency must have high prestige and excellent diplomatic relations with others to project its economic dominance. With its many free trade agreements and alliances worldwide, the US is a good example of a highly positive scenario.
It is not a coincidence that the US has few enemies among the nations of the world. Its military power acts as a deterrent to foreign aggression. Apart from a few ideologically driven adversaries, the US continues to maintain solid relationships with many nations, in spite of the fact that jealousy of its unchallenged dominance could cause antagonism among world leaders.
However, the global community’s usage of the US Dollar for everything from reserves, forex transaction volume, outstanding foreign currency debt instruments, cross-border deposits, and cross-border loans speaks volumes, regardless of growing resistance to US dominance. The Federal Reserve in the US has plotted an index based on these five factors, and it demonstrates the resiliency, stability, and support by worldwide users, as depicted below:
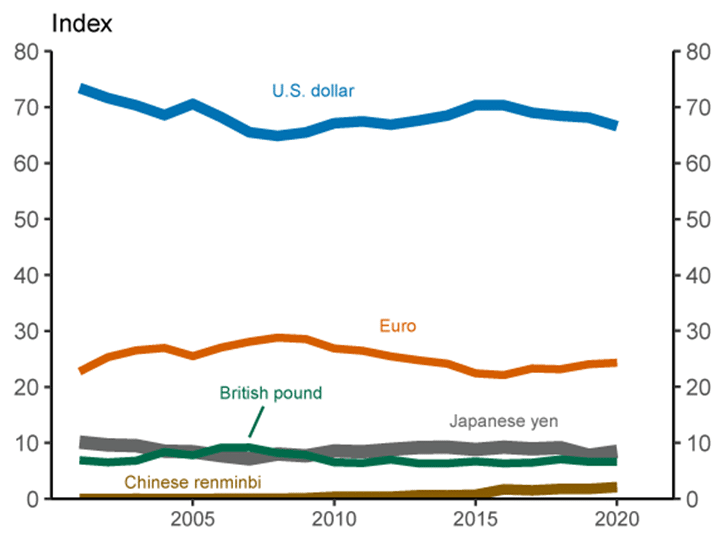
Chart courtesy of www.FederalReserve.gov
Is the US Dollar under Threat of Being Replaced as the World’s Reserve Currency?
With the rise of China, oil-exporting states, and other large commodity exporters on the global trade scene, discussions and press headlines often predict the demise of the USD as the world’s predominant reserve currency. The rise of the Euro, inflation, and the deepening of the overall debt positions of the United States have also fanned these flames. Still, the consensus of economic experts is that these threats are not credible.
There are several reasons for discounting these threats to the pre-eminence of the US Dollar. The first thing to consider is that the USD is 60% of present reserve holdings, while its nearest competitor, the Euro, has but 20%. There has also not been a rush to conduct global trade in another currency. For trading contracts in North America, Asia-Pacific, and the rest of the world, the shares contracted in USD are 96%, 74%, and 79%, respectively.
Yet, negative arguments arise, primarily because of the steady decline in the USD share of global reserves from 65% to 60% over the last 25 years. These gradual shifts, however, are explainable. As the global economy has become more interconnected and interdependent, the regimes of many developed countries have also become more stable, with higher returns and lower volatility. The US is no longer the only developed country capable of dependable governance, economic stability, and sound finances. These traits have always garnered support from foreign investors.
Where have the shifts occurred? Based on analyses by staff at the IMF, the Euro, the Yen, and the British Pound do not reflect the associated share increases in non-US reserve positions. As much as the Chinese economy has grown over the past 50 years, reserves held in Renminbi only account for 25% of the shift away from the USD. The remainder is comprised of increasing reserves held in smaller but highly successful countries on the international scene, including Australia, South Korea, Canada, and Sweden.
The principal reason, however, for the USD to remain the world’s reserve currency is that it has the backing of the strength and stability of the US economy. Yes, deficits have risen due to the Covid pandemic, but so have deficits around the world. Trends for the USD Index have also reversed after the Great Recession, reflecting a strong resurgence in support for it going forward, as depicted below:
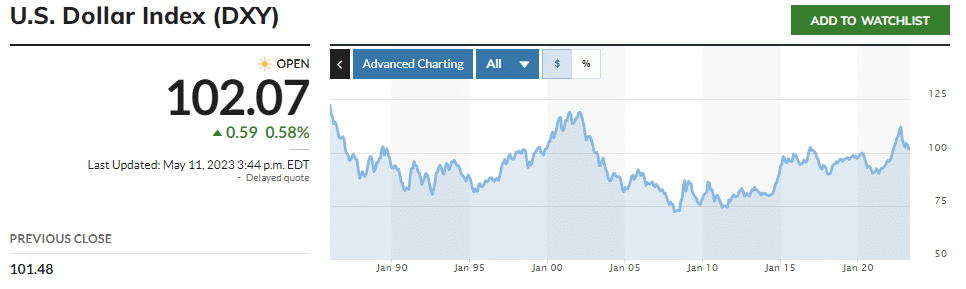
Chart of the USD Index courtesy of Marketwatch.com
Summary
According to recent BIS statistics, 88% of all transactions conducted in our foreign exchange market have the USD planted squarely as half of all traded currency pairs. The dominance of the US Dollar, the strength of the US economy, and the country’s political stability have led to it being the world’s reserve currency. The USD’s stability supports a global trade system where contracts are also conducted in this currency.
Can the US Dollar retain its dominance as the world’s premier reserve currency? Critics of the current reserve system have proposed alternatives, but experts discount these threats as not credible. Any declines noted in existing USD reserve shares are due to a balancing of risk concerns by central bankers by including several additional participants with stable economies, effective government rule, and reliable financial policies. The USD will remain the King of Reserves for the foreseeable future.
Choose one of our Top Forex Brokers
| Broker | Features | Regulator | Platforms | Next Step | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2014 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2014 |
|
FSPR | MT4 | ||
 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2006 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2006Europe* CFDs ar... |
|
ASIC, FSA, FSB, MiFID | MetaTrader4, Sirix, AvaOptions, AvaTrader, Mirror Trader | ||
 Between 74-89% of CFD traders lose
Founded: 2010 Between 74-89% of CFD traders lose
Founded: 2010Between 74-89 % of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs |
|
ASIC, FCA | MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader | ||
 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2009, 2015, 2017 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2009, 2015, 2017 |
|
ASIC, CySEC, IFSC | MT4 Terminal, MT4 for Mac, Web Trader, iPhone/iPad Trader, Droid Trader, Mobile Trader, MT5 | ||
 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2006 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2006 |
|
CySEC, DFSA, FCA, FSB, SIA | MetaTrader4, MetaTrader5, cTrader, FxPro Edge (Beta) | ||
 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2011 Your capital is at risk
Founded: 2011 |
|
CySEC, FSC, FSCA, MISA | MT4, MT5, OctaTrader | ||
Forextraders' Broker of the Month
BlackBull Markets is a reliable and well-respected trading platform that provides its customers with high-quality access to a wide range of asset groups. The broker is headquartered in New Zealand which explains why it has flown under the radar for a few years but it is a great broker that is now building a global following. The BlackBull Markets site is intuitive and easy to use, making it an ideal choice for beginners.
